INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
What is Surface Mounting Technology (SMT) in PCB Assembly?
When speed matters and space is tight, Surface Mounting Technology (SMT) is the go-to method for assembling printed circuit boards. Instead of using wire leads and bulky components, SMT allows engineers to mount components directly onto the board’s surface. This streamlined approach is faster, more compact, and built for precision, making it a favorite for everything from medical devices to aerospace systems.
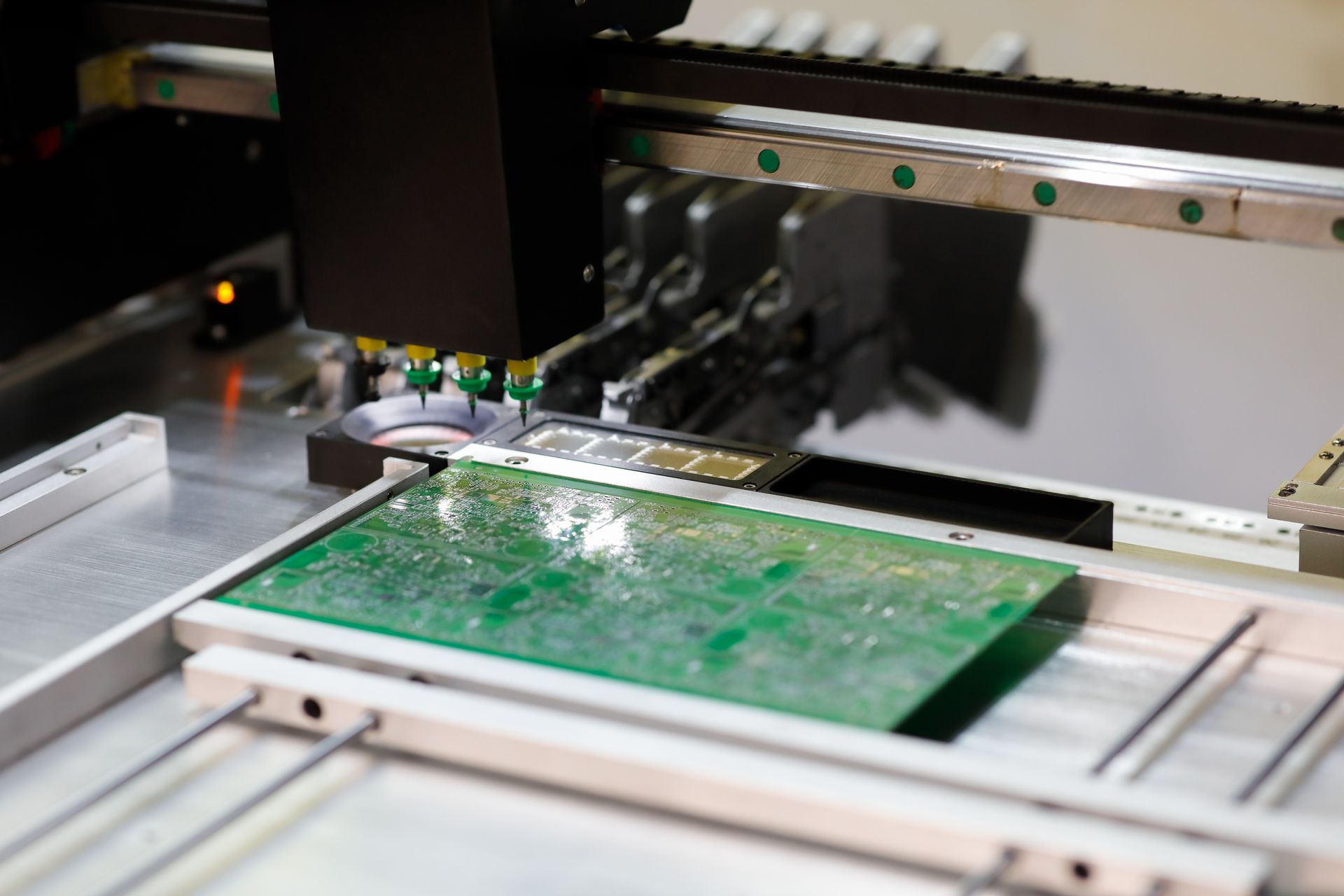
Today, SMT has become the backbone of modern electronics manufacturing because it scales from a single prototype to short production runs with ease. For teams racing to validate a concept or iterate on a design, SMT is the kind of manufacturing firepower that turns tight timelines into workable ones. And if you’re looking for a fast, U.S.-based partner who gets it right the first time, Ninja Circuits is ready to help.
Understanding Surface Mounting Technology (SMT)
Surface Mounting Technology, or SMT, is the process of placing and soldering electronic components directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike traditional through-hole assembly, which requires drilling holes and inserting component leads, SMT skips the drill bit and goes straight to placement, saving time and board space.
SMT components, often called surface-mount devices (SMDs), are smaller and lighter than their through-hole counterparts. They’re placed using precision pick-and-place machines, then soldered using reflow ovens or advanced techniques like vapor-phase reflow. The result? Dense, high-performance circuit boards that support faster signal transmission, lower inductance, and tighter design tolerances.
SMT is the industry standard for most
PCB assemblies, especially in compact, high-speed, or high-volume applications. It’s the reason your smartphone fits in your pocket and your prototype doesn’t take weeks to build. It’s lean, it’s fast, and it’s built for engineers who can’t afford slow.
How Surface Mounting Works in PCB Assembly
The
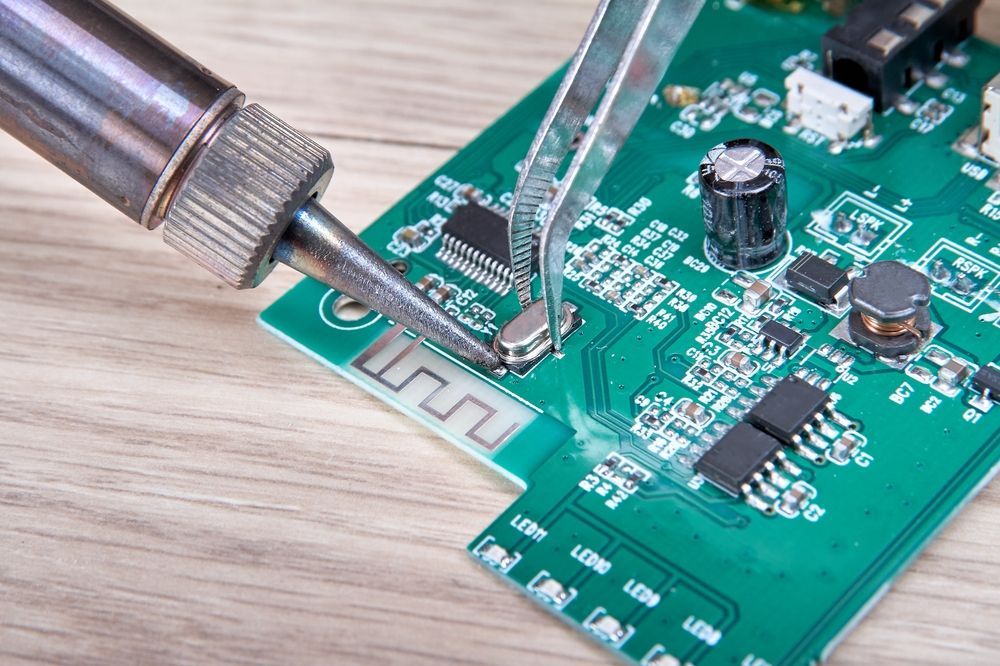
SMT assembly process starts with a clean, solder-paste-coated PCB. Using a stainless steel stencil, solder paste is applied only where components will land (think of it like screen-printing for electronics). Then, high-speed pick-and-place machines position each surface-mount device (SMD) on the board with sub-millimeter accuracy.
Once placed, the entire board enters a reflow oven, or in high-precision cases like at Ninja Circuits, a vapor-phase reflow system, where heat melts the solder and bonds the components in place. This results in strong, reliable electrical and mechanical connections without the need for through-hole leads.
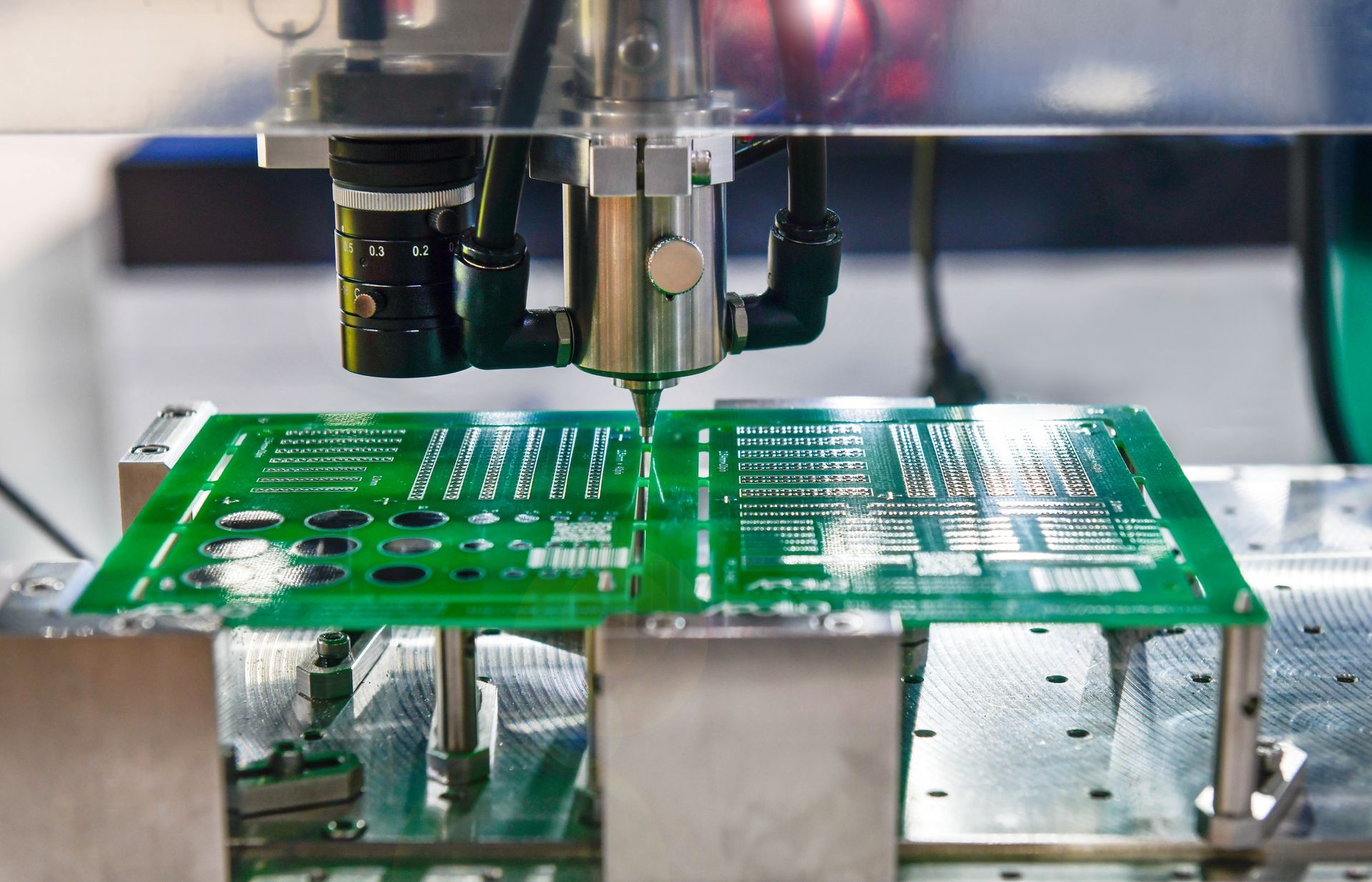
For quality assurance, assembled boards often go through 3D automated optical inspection (AOI) to catch any misalignments or defects before final testing. It’s a precise, repeatable process, and it’s ideal for fast prototyping, tight pitch components, and miniaturized electronics where every millimeter counts.
Pros and Cons of Surface Mount Assembly
Surface Mount Assembly offers serious advantages, especially for engineers focused on speed, precision, and board density. SMT allows for smaller components, which means more functionality packed into less space, which is essential for compact designs like wearables, drones, or medical devices.
It also supports automated placement, making high-speed, high-volume assembly not only possible, but efficient. With no holes to drill, turnaround times are faster and costs can drop significantly, especially in prototype and short-run builds.
But SMT isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Components are harder to manually solder or rework, especially without specialized tools. Thermal management can be trickier on dense boards, and not every component type comes in a surface-mount package, which is why some designs still use a mix of SMT and through-hole.
Still, for most modern designs, SMT is the go-to. And when paired with precise tools and experienced hands (hint: that’s us), it delivers fast, clean results every time.
Key Industry Applications
SMT is the workhorse behind nearly
every modern electronic device, from the critical to the everyday. Here’s where it shines:
Medical Devices
Miniaturized circuits for wearables, imaging tools, diagnostic equipment, and implantables.
Aerospace & Defense
Lightweight, high-reliability boards for mission-critical systems, avionics, and communications.
Consumer Electronics
High-density layouts for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and connected home tech.
Industrial Automation
Durable SMT boards built to handle vibration, temperature swings, and 24/7 uptime.
Robotics & Drones
Compact, power-efficient PCBs for motion control, sensors, and AI processors.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Ultra-compact designs powering smart sensors, edge devices, and connected infrastructure.
Automotive & EV
Advanced driver-assist systems, battery management, and onboard computing modules.
Telecommunications
High-frequency RF circuits and dense digital signal paths in compact enclosures.
At Ninja Circuits, we see SMT demand surge across R&D teams and OEMs building prototypes for everything from EV components to edge computing nodes.
Why SMT Is Ideal for Prototypes and Short Runs
When you’re prototyping, every hour matters. SMT speeds up the build cycle by skipping the drill-and-stuff process used in through-hole assembly, making it easier to iterate quickly and test designs in real-world conditions. With automated placement and reflow, you can go from schematic to physical board faster, especially when you're working with a U.S.-based partner like Ninja Circuits who knows how to move.
SMT also allows for tighter layouts, which means you can pack more function into less space. And because surface-mount components are widely available and affordable, it’s easier to source parts that match your design goals and BOM constraints.
For short runs, SMT offers the perfect balance of efficiency and flexibility. If you're testing a board revision or building a small pilot batch, surface mount assembly helps you stay agile without sacrificing quality.
Partner with Ninja Circuits for Precision SMT Assembly
When you’re working against a tight deadline or pushing the limits of a design, you need an assembly partner who gets it right the first time. At Ninja Circuits, we specialize in fast-turn SMT assembly for engineers who can’t wait weeks to see their ideas take shape.
We’ve helped businesses refine prototypes, validate new products, and overcome the challenges of short-run design by focusing on what matters most: speed, precision, and reliability. Our U.S.-based facility is built for quick-turn flexibility and engineered to support evolving designs without delay. With vapor-phase reflow, 3D AOI, and an engineering-first mindset driving every build, we deliver clean, functional boards that are ready to perform.
If you need it fast, call Ninja. Start Your Prototype or
Request a Quote to get your build moving.
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS